3 Miles In 29 Minutes
Pace Calculator
Employ the following calculator to guess the footstep for a multifariousness of activities, including running, walking, and biking. The calculator can too exist used to estimate the fourth dimension taken or distance traveled with a given pace and fourth dimension or distance.
Multipoint Pace Calculator
The following reckoner tin determine the pace of segments of a run (or other activity) for those with access to the time at intermittent points during the run. For example, if a person runs from point A to signal B, then to point C, records the fourth dimension at each bespeak, and afterwards determines the altitude between those points (using many available websites, applications, or maps), the multipoint calculator can determine how fast the person traveled between each pair of points, allowing utilize for grooming purposes; a person tin run the same route (or distance) repeatedly and rail pace over that given road, enabling comparison of times between each segment (or lap) to identify areas for potential comeback.
| Distance | Time (hh:mm:ss) | ||
| ane. | |||
| 2. | |||
| 3. | |||
| iv. | |||
| 5. | |||
| 6. | |||
| 7. | |||
| eight. | |||
| 9. | |||
| x. | |||
| 11. | |||
| 12. | |||
| Your Preferred Footstep Unit | |||
 | |||
Pace Converter
| | = | ? | |
 | |||
Terminate Time Calculator
The following calculator can be used to estimate a person'southward finish time based on the time and distance covered in a race at the point the computer is used.
| Electric current Distance Traveled | |
| Elapsed Fourth dimension | hh:mm:ss |
| Total Distance | |
 | |
Typical Races and Earth Record Paces
| Category | Men'south World Tape Stride | Women's World Record Footstep |
| 100 meters | 2:35/mile or 1:36/km | two:49/mile or 1:45/km |
| 200 meters | 2:35/mile or 1:36/km | ii:52/mile or 1:47/km |
| 400 meters | 2:54/mile or 1:48/km | 3:12/mile or 1:59/km |
| 800 meters | iii:23/mile or two:06/km | 3:48/mile or 2:21/km |
| 1,500 meters | three:41/mile or two:17/km | 4:07/mile or 2:34/km |
| 1 mile | three:43/mile or two:19/km | 4:xiii/mile or 2:37/km |
| 5K | 4:04/mile or ii:31/km | four:34/mile or 2:l/km |
| 10K | 4:14/mile or 2:38/km | 4:45/mile or ii:57/km |
| Half Marathon (xiii.eleven miles / 21.098 km) | 4:27/mile or 2:46/km | four:58/mile or 3:05/km |
| Marathon (26.22 miles / 42.195 km) | 4:41/mile or 2:55/km | 5:10/mile or 3:thirteen/km |
Training Through Stride and Eye Charge per unit
Pace is a rate of activity or movement, while center rate is measured every bit the number of times that a person's eye contracts over a minute. Pace and middle rate take a positive correlation; higher pace corresponds to higher centre charge per unit. The utilise of both in training tin help a person amend functioning, avoid over-grooming, as well as track progress and fitness over fourth dimension.
Measuring and Estimating Heart Rate and Heart Rate Zones:
Heart rate can exist measured in unlike ways, from using devices such as heart charge per unit monitors, to simply looking at a scout while measuring pulse at some peripheral point such as the wrist or neck. Some of the more than notable measurements of heart rate include resting heart rate and maximum heart rate, which are oftentimes used to judge specific target centre charge per unit zones to make up one's mind different levels of exercise.
Typical developed resting heart rates (RHR) are ordinarily cited to range from 60-100 beats per minute (bpm), though there is some argument that normal RHRs really fall inside the range of fifty-xc bpm. More often than not, a lower RHR indicates more efficient middle function, though RHRs that are lower than 50 bpm can exist a sign of an underlying heart status or disease. The same is truthful of RHRs above xc bpm.
Maximum heart rate (MHR) is virtually accurately measured using a cardiac stress test, which involves measuring a person's center function (including heart rate) at periodically increasing levels of do. These tests typically range from ten to twenty minutes in elapsing, which can be inconvenient. As such, there are many estimates for MHR based on age, which is strongly correlated with heart rate, though there is little consensus regarding which formula should be used. The most ordinarily cited formula for calculating MHR is:
MHR = 220 – age
Although it is the near commonly cited formula, and is often used to decide center rate training zones, it does not take a reference to any standard departure, and is non considered a adept predictor of MHR by reputable health and fitness professionals. Furthermore, MHRs vary significantly between individuals, even those with highly similar training and age within the aforementioned sport. Nevertheless, MHR determined using the higher up formula is oft used to prescribe exercise grooming middle charge per unit ranges, and can exist beneficial as a reference. Notation that an exercise intensity level of 60-lxx% of maximum center rate is considered the ideal range for called-for fat. Refer to the figure below for further detail.
Exercise intensity levels and typical heart rates associated with said levels based on age
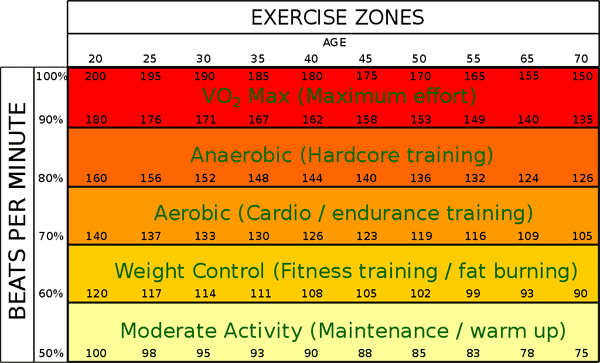
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Practice:
Aerobic and anaerobic exercise are frequently mentioned in the context of endurance training and running. These types of exercise mainly differ based on the duration and the intensity of muscular contractions and the mode in which energy is generated inside the muscle. Generally, anaerobic exercises (~fourscore-90% MHR) involve short, intense bursts of activity while aerobic exercises (~lxx-80% MHR) involve light activeness sustained over a long period of time. An do intensity level of 55-85% of MHR for 20-30 minutes is generally recommended to accomplish the best results from aerobic practice.
In solely aerobic practise, there is sufficient oxygen for a person's muscles to produce all the necessary energy for the practise. In contrast, in anaerobic exercise, the cardiovascular system cannot supply muscles with oxygen quickly enough, and muscles break down sugar to supply the necessary free energy, resulting in excess of lactate (a byproduct of glucose metabolism). Excess lactate causes the called-for awareness in muscles typical of anaerobic exercises and eventually makes the continuation of exercise not possible if backlog lactate is not allowed sufficient time to exist removed from the bloodstream. Note that although lactate is as well produced in aerobic weather condition, information technology is used almost as quickly as it is formed at low levels of practise, and only trace amounts leak into the bloodstream from the muscles.
Understanding aerobic practise is specially important when training for a long-distance activity such as a marathon. Determining a pace that can exist maintained while using energy primarily derived through aerobic ways, referred to as an "aerobic threshold footstep," helps maintain a residual between fatty and carbohydrate utilization. This footstep requires a relatively low level of intensity, and is usually maintainable for a few hours. Increasing aerobic threshold pace allows for a faster sustainable pace and is a large aspect of many marathon training programs.
An anaerobic threshold stride is divers by some as the threshold at which glycogen, rather than oxygen, becomes the master source of energy for the body. Note that while anaerobic grooming volition result in a person condign more fit overall, it is not necessarily ideal preparation for a marathon, since an anaerobic pace is non sustainable for long periods of time. This is not to say that a person should not perform any anaerobic training, as training at or slightly in a higher place their anaerobic threshold (the level of exercise intensity at which lactic acid builds up more chop-chop than it can exist removed from the bloodstream) tin also be beneficial.
Similarly to eye rate, the almost accurate mode to determine these thresholds is through testing within a lab setting. Notwithstanding, both aerobic and anaerobic thresholds tin can also exist estimated using a number of different methods, some of which involve the employ of a heart rate monitor. According to a 2005 study, the most accurate way to determine anaerobic threshold (outside of blood work in a lab) is a thirty-infinitesimal time trial in which heart charge per unit is monitored. In this fourth dimension trial, a person must run at maximum effort, averaging their eye rate over the final 20 minutes of the run. The average centre charge per unit over the terminal 20 minutes is an interpretation of the person's anaerobic threshold heart rate, also known as lactate threshold eye charge per unit (LTHR). Information technology is important that the time trial be performed lonely. If it is done in a grouping setting, the duration must be increased to threescore minutes rather than 30 minutes. Aerobic threshold heart charge per unit tin be estimated by subtracting thirty beats per minute from the anaerobic threshold heart rate.
Essentially, threshold training involves training to postpone the bespeak at which lactate starts to build upward in the bloodstream, which finer postpones the point of fatigue, potentially allowing a person to run farther and faster.
3 Miles In 29 Minutes,
Source: https://www.calculator.net/pace-calculator.html
Posted by: farmerreanday.blogspot.com


0 Response to "3 Miles In 29 Minutes"
Post a Comment